Webhooks
A webhook sends a POST request to a specific URL every time an API is saved or published in API Hub for Design. You can use webhooks to notify external systems when your API definitions are updated and to trigger your own custom actions based on events from API Hub for Design.
Once you configured webhooks for a specific version of an API, you can carry them over to new versions of this API.
Add a webhook
To add or change webhooks, you must be have the Owner or Designer role.
Open the API in the API Hub for Design editor.
If the API has several versions, select the version for which you want to add a webhook.
Click the API name, switch to the Integrations tab, and click Add New Integrations:
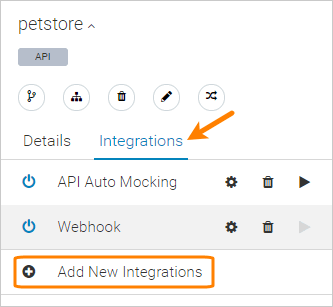
Select Webhook from the list of integrations.
Configure the webhook:
Name – A display name for the webhook.
Payload URL – The URL where API Hub for Design will send a POST request. Make sure to include
http://orhttps://at the beginning.The server that this URL points to must be accessible from the public Internet and allow connections from our IP addresses.
Content Type – Specifies the data format and the
Content-Typeheader of webhook requests. Possible values:JSON (
application/json)form data (
application/x-www-form-urlencoded)
Lifecycle Events – Select one or more events that will trigger the webhook. The available events are:
After API/version saved.
After API/version published.
Additional Headers – Custom HTTP headers (such as authorization headers) to be sent with each webhook request. Headers must be in the
name: valueformat, for example,Authorization: Bearer abcde12345. Click to add a new header to the list.
to add a new header to the list.Enable – You can unselect this check box to temporarily disable the integration without deleting it.
Click Create, then Done.
POST data
When an API version is saved or published, API Hub for Design sends a POST request to the specified URL. The User-Agent for requests will be Apache-HttpClient/Swagger. The POST payload contains the API path in API Hub for Design, the action that triggered the webhook and the JSON-formatted definition of the API.
Data in JSON webhooks looks like the following:
{
"path": "/apis/username/api-name/1.1",
"action": "after_api_version_saved",
"definition": {
"swagger": "2.0",
"info": {
"description": "This is a sample Petstore server ...",
"version": "1.1",
"title": "Swagger Petstore"
},
"host": "petstore.swagger.io",
...application/x-www-form-urlencoded webhooks include this JSON data as a single form field named payload. The decoded body looks like this:
payload = {"path":"/apis/username/api-name/1.1","action":"after_api_version_saved","definition":{"swagger":"2.0","info":{"description":"This is a sample Petstore server ...The raw body looks like this:
payload=%7B%22path%22%3A%22%2Fapis%2Fusername%2Fapi-name%2F1.1%22%2C%22action%22%3A%22after_api_version_saved%22%2C%22definition%22%3A%7B%22swagger%22%3A%222.0%22%2C%22info%22%3A%7B%....
Troubleshooting
Integration failures, including webhooks errors, are indicated by the Integration Errors message at the top of the editor. Click this message to see if the problem is with webhooks. Below are some things to check.
Make sure the webhook URL is correct, reachable from the public Internet (specifically, from our IP addresses), and accepts POST requests.
If the webhook URL requires specific authorization headers, specify them in the Additional Headers option.
If the webhook URL is
https://, it must use an SSL certificate from a public CA. API Hub for Design does not support self-signed and privately signed certificates. However, such certificates are supported by SwaggerHub On-Premise.