Example NodeJS Provider - Postman
Source Code
https://github.com/pactflow/example-bi-directional-provider-postman

Overview of Example
This is an example of a NodeJS "Product" API Provider that uses Postman, Pact, API Hub for Contract Testing and GitHub Actions to generate and publish Pact provider contracts.
It performs pre-deployment cross-compatability checks to ensure that it is compatible with specified consumers using the Bi-Directional contract capability of API Hub for Contract Testing.
See the full API Hub for Contract Testing Bi-Directional Workshop for which this can be substituted in as the "provider".
Key points
It:
Is an API written in Express JS
Has a Postman 2.1 collection (see
./test/API Hub for Contract TestingProductsAPI.postman_collection.json)Uses Newman to test the API against the postman collection
Uses Postman2OpenAPI to convert a Postman collection to an OAS for use in the bi-directional contracts feature.
What is uploaded to API Hub for Contract Testing is an OpenAPI specification that represents what you actually tested with Postman, to give us confidence it is compatible with a Pact consumer.
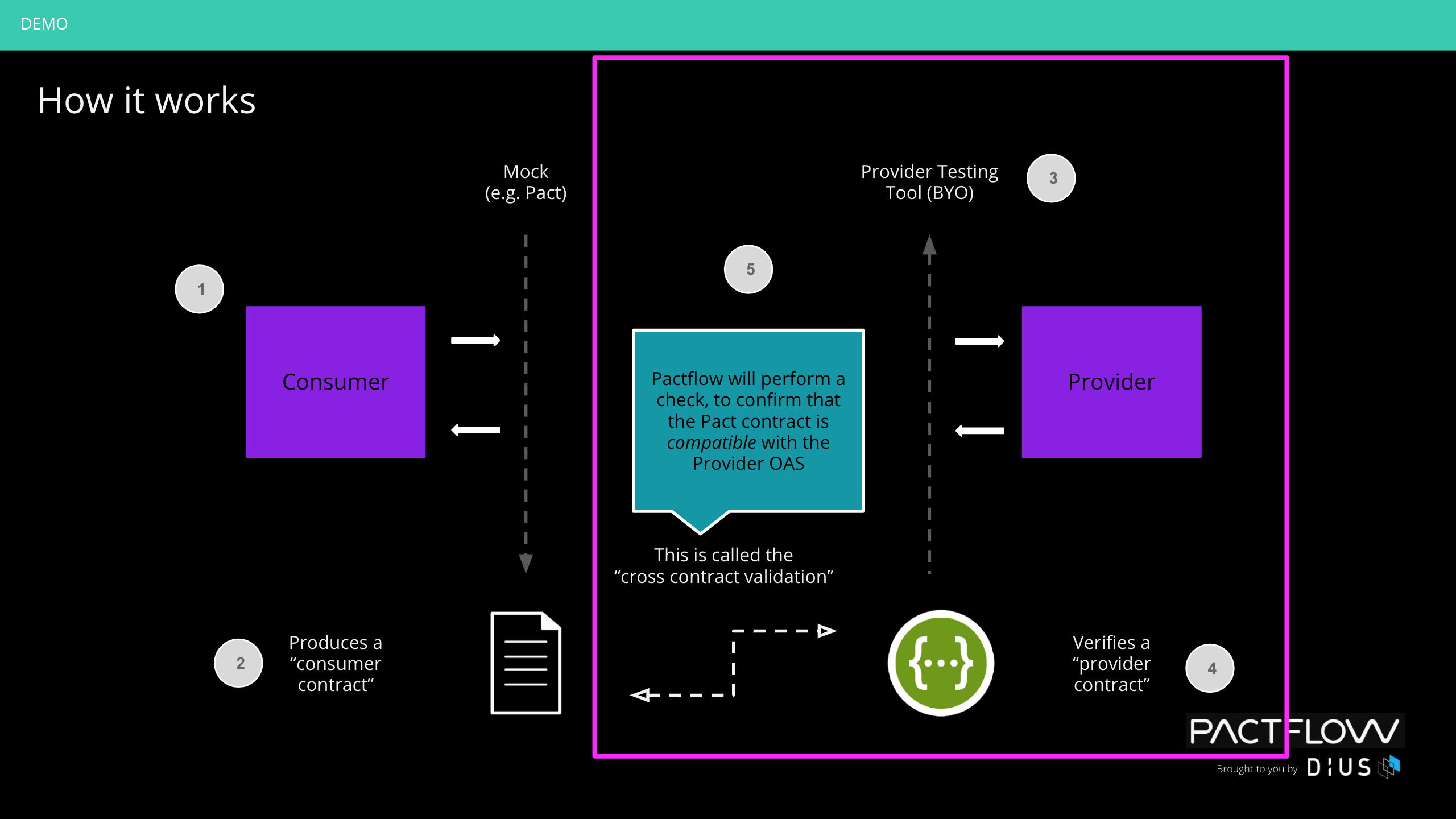
Overview of Part of Bi-Directional Contract Testing Flow
In the following diagram, you can see how the provider testing process works.
When we call "can-i-deploy" the cross-contract validation process kicks off on API Hub for Contract Testing, to ensure any consumer consumes a valid subset of the OAS for the provider.
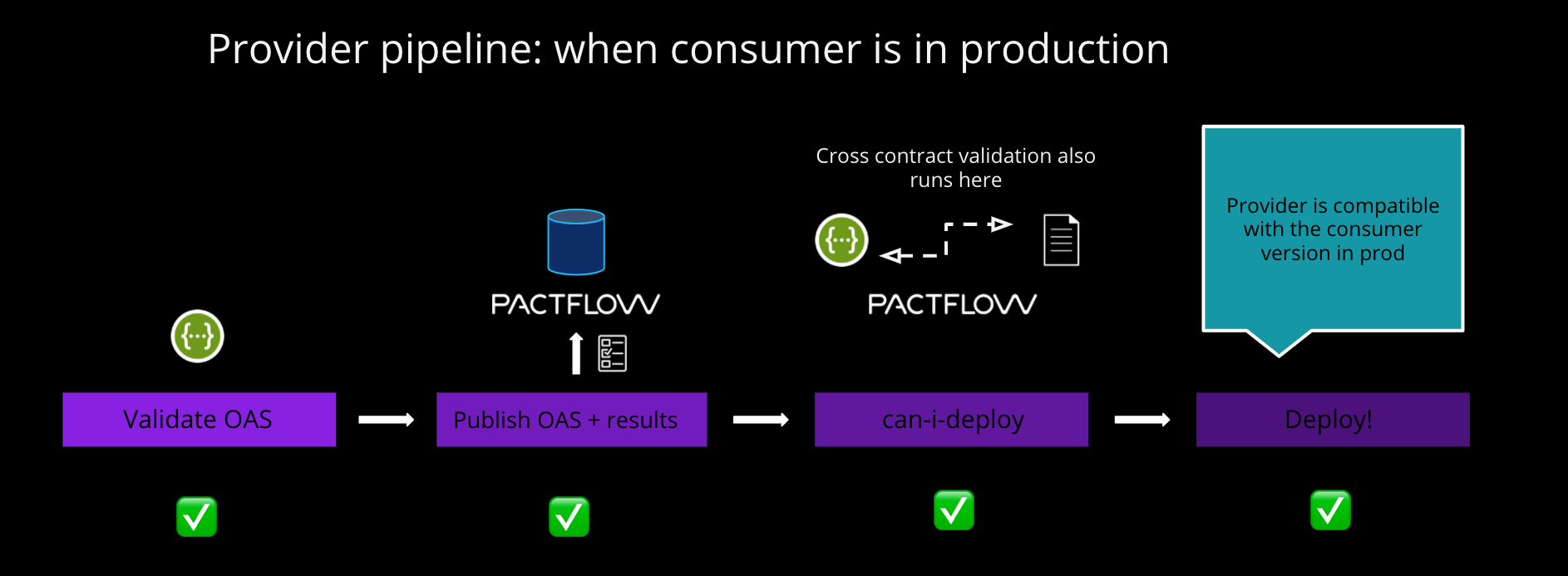
The project uses a Makefile to simulate a very simple build pipeline with two stages - test and deploy.
When you run the CI pipeline (see below for doing this), the pipeline should perform the following activities (simplified):
Test
Run tests to check spec compliance with openAPI spec
Create branch tag via Pact CLI
Publish openAPI spec, along with a version with the name of the current branch
Check if we are safe to deploy to Production with
can-i-deploy(ie. has the cross-contract validation has been successfully performed)
Deploy (only from <main|master>)
Deploy app to Production
Record the Production deployment in the Pact Broker
Compatible with Consumers
This project is currently compatible with the following consumers(s):
See Environment variables on how to set these up.
Pre-requisites
Software:
Environment variables
To be able to run some of the commands locally, you will need to export the following environment variables into your shell:
PACT_BROKER_TOKEN: a valid API token for API Hub for Contract TestingPACT_BROKER_BASE_URL: a fully qualified domain name with protocol to your pact broker e.g., https://testdemo.pactflow.io
Usage
Steps
make install- install project dependencies
Run each step separately
make test_and_publish- tests the provider and publishes provider contracts to API Hub for Contract TestingThis will perform the following 2 calls
make testmake publish_provider_contract
make can_i_deploy- runs can-i-deploy to check if its safe to deploy the providermake deploy- deploys the app and records deployment
or run the whole lot in one go
make ci- run the CI process, but locally (uses Docker by default)
Installing alternate pact CLI tools.
If you don't have docker, you can use one of the ruby tools. The standalone, doesn't require that you install Ruby on your host machine.
make install-pact-ruby-cli- installs the pact ruby CLI toolmake install-pact-ruby-standalone- installs the pact standalone CLI depending on your platformmake uninstall-pact-ruby-standalone- uninstalls the pact standalone CLI
Using alternate pact CLI tools.
PACT_TOOL=docker make ci- run the CI process, using the pact Docker CLI toolPACT_TOOL=ruby_standalone make ci- run the CI process, using the pact standalone CLI toolPACT_TOOL=ruby_cli make ci- run the CI process, using the pact ruby CLI tool
OS/Platform specific considerations
The makefile has been configured to run on Unix/Windows and MacOS based systems, and tested against Github Actions
They can be run locally on Unix/Windows and MacOS, or on Windows via WSL2 or a shell with bash.
Caveats
OAS is generated by the examples attached to each request. If there are mulitple overlapping paths, the last one will clobber earlier ones (use the Postman examples feature to overcome this)
Postman tests are attached to the "item" level, not the examples. So it's possible to put in examples that don't actually match reality and aren't tested.
Other examples of how to do this form of testing
TBC
Found an issue?
Reach out via a GitHub Issue, or reach us over in the Pact foundation Slack.
